40 cell membrane
Cell: Cell WebCell Cell publishes findings of unusual significance in any area of experimental biology, including but not limited to cell biology, molecular biology, neuroscience, immunology, virology and microbiology, cancer, human genetics, systems biology, signaling, and disease mechanisms and therapeutics. More This is a Transformative Journal Cell (biology) - Wikipedia WebThe cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life forms. Every cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, and contains many biomolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA, as well as many small molecules of nutrients and metabolites. The term comes from the Latin word cellula meaning 'small room'.
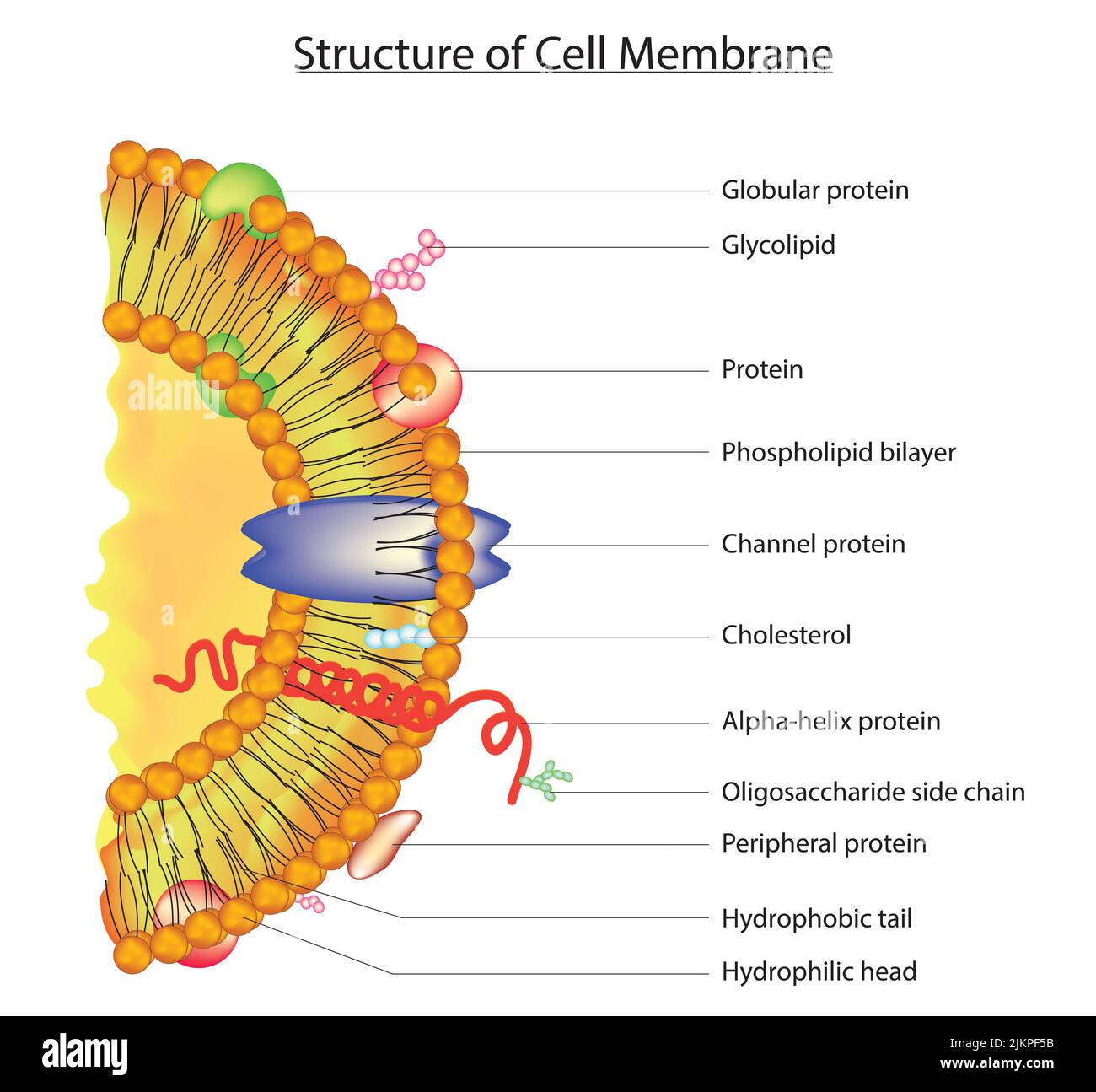
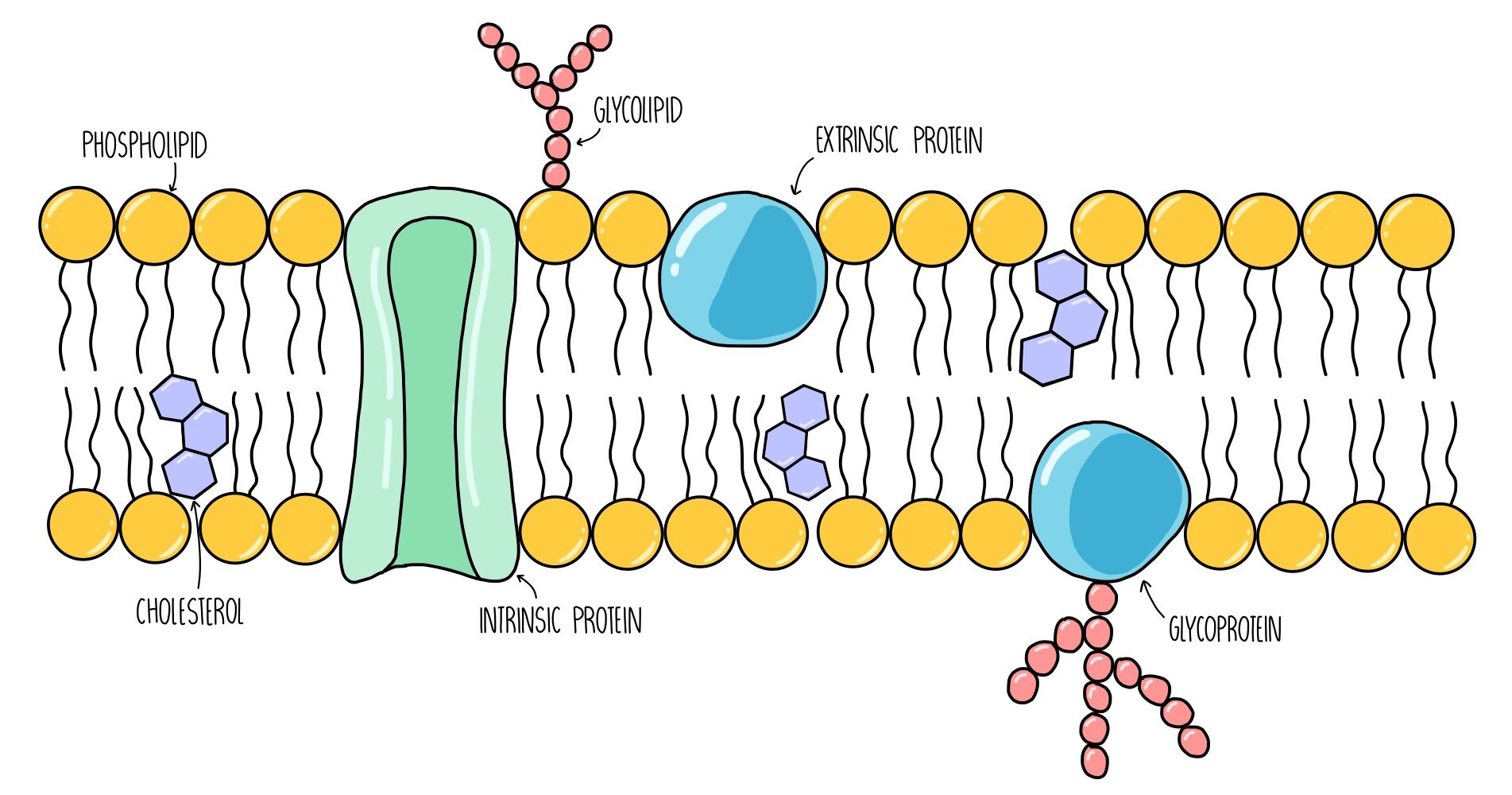
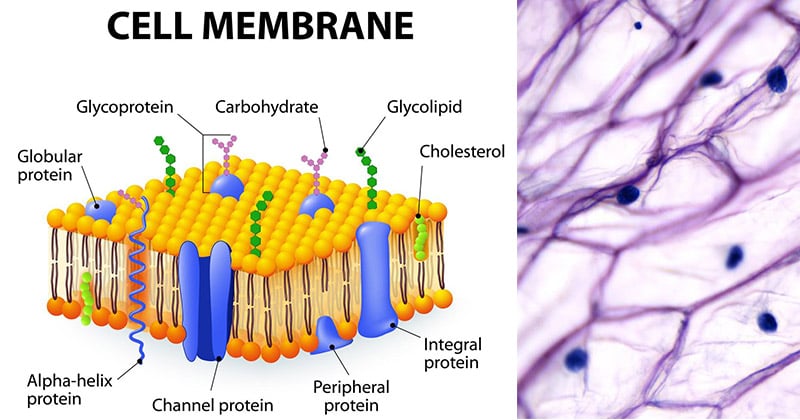
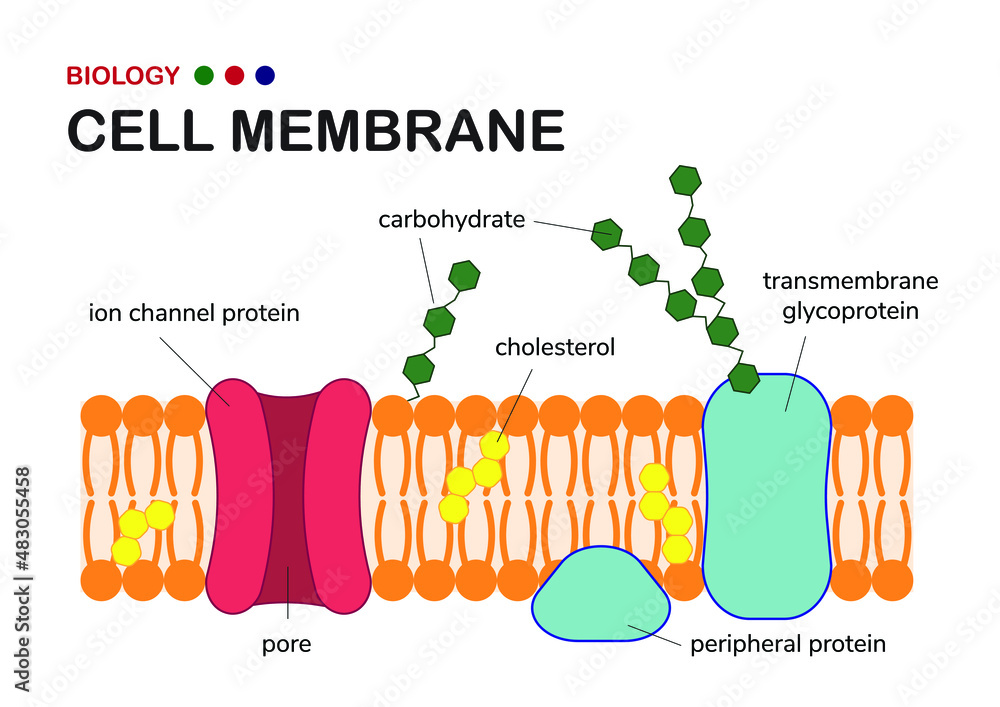
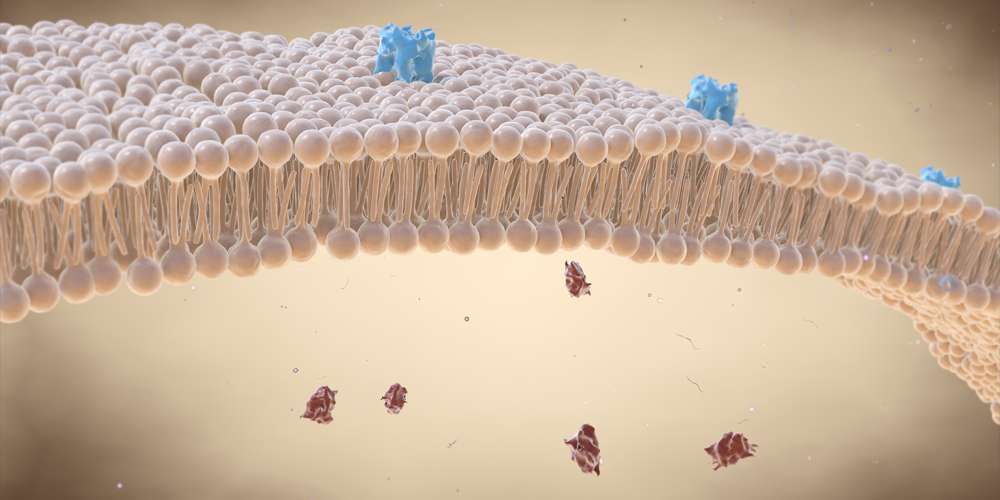
Cell Membrane - The Definitive Guide | Biology Dictionary Oct 19, 2020 · Cell Membrane Definition. The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a double layer of lipids and proteins that... Function of the Cell Membrane. The cell membrane gives the cell its structure and regulates the materials that enter and... Structure of the Cell Membrane. Phospholipid ...
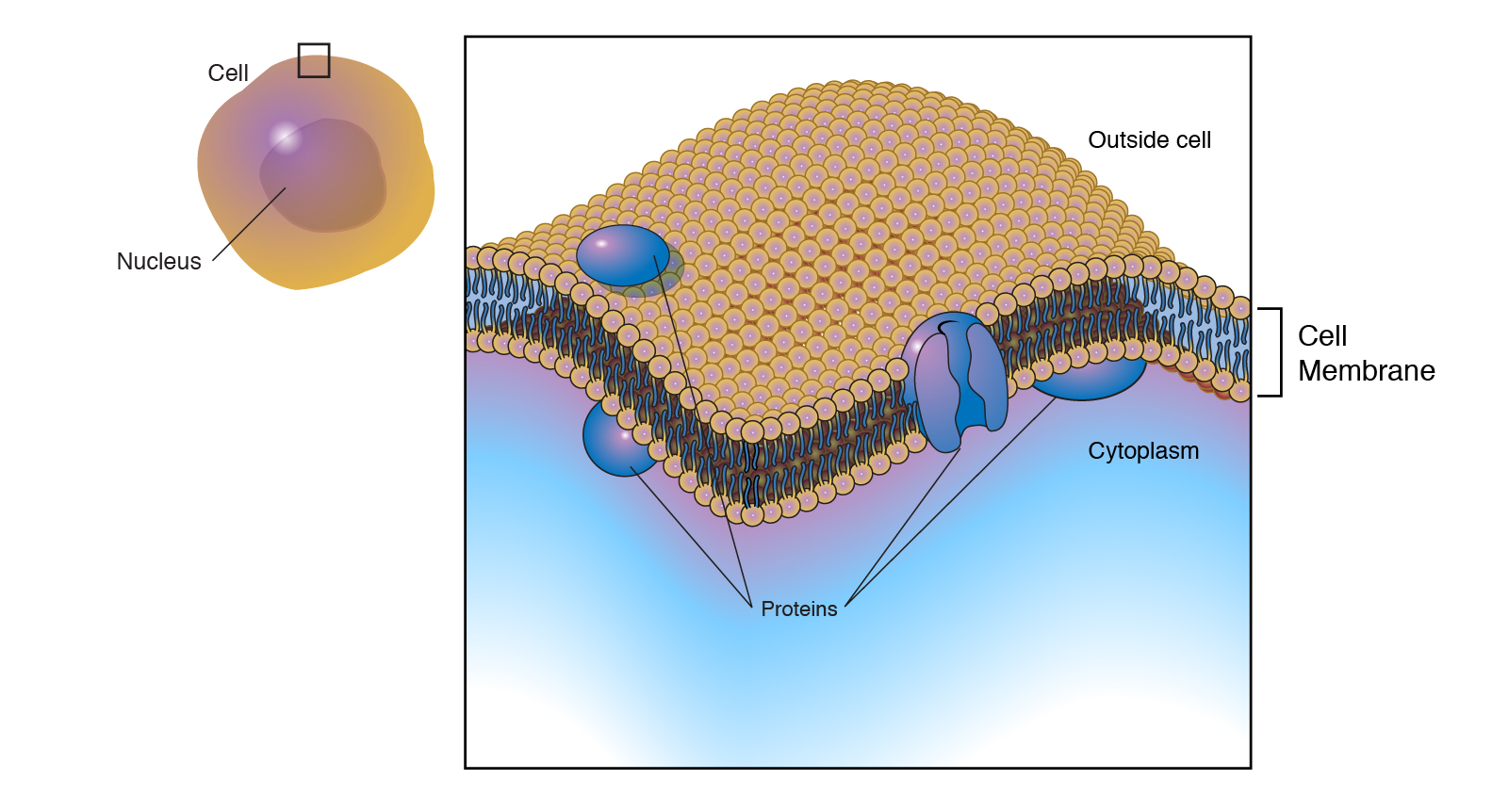
Cell membrane
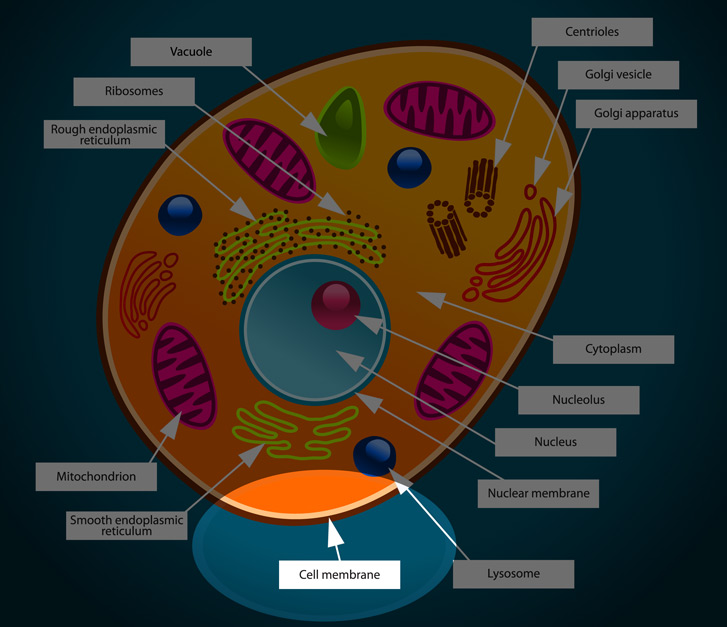
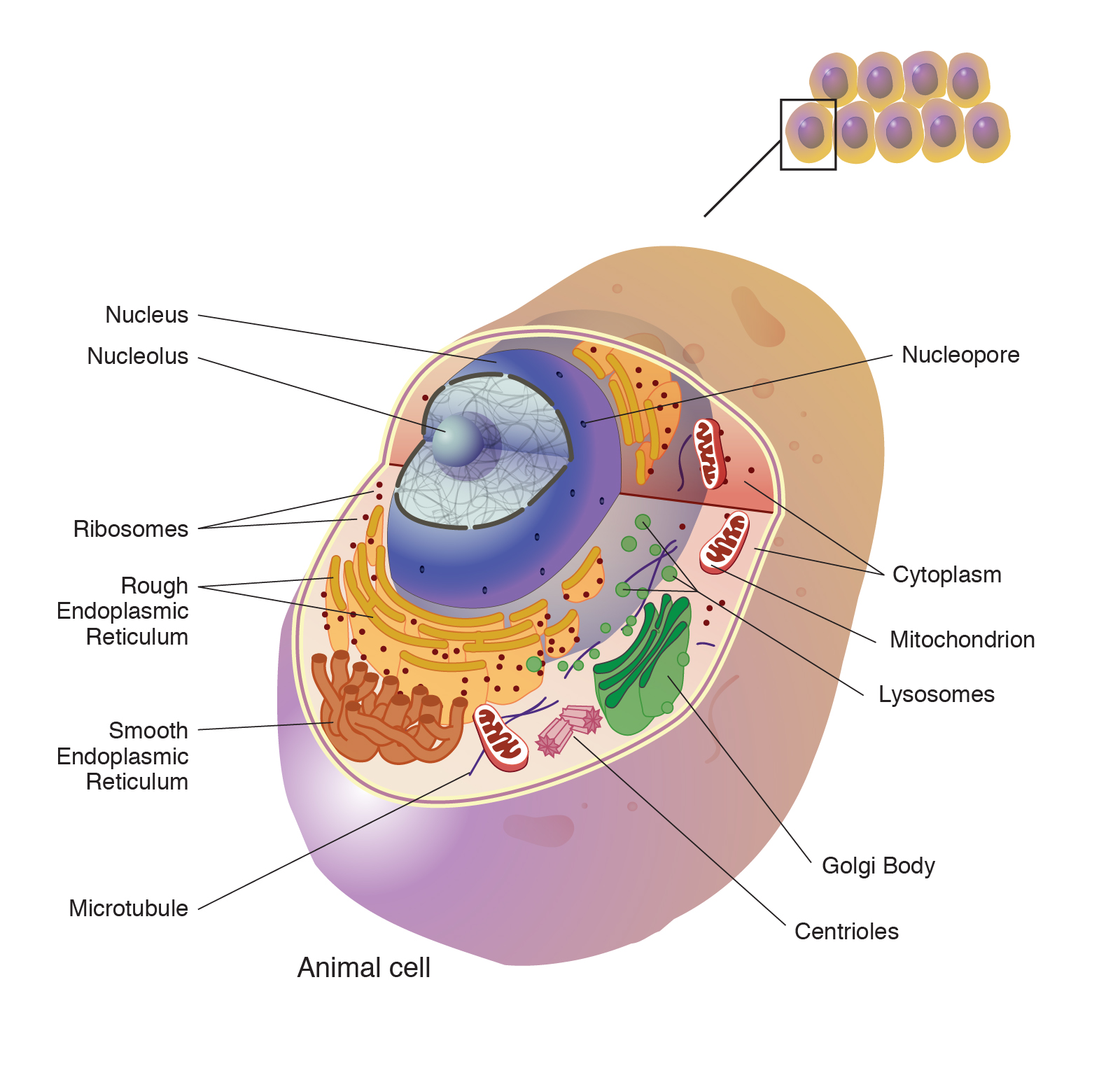
Fluid mosaic model: cell membranes article (article) | Khan... Cell membrane introduction. Cell membrane overview and fluid mosaic model. Fluid mosaic model: cell membranes article. Plant cell walls. The extracellular matrix and cell wall. Membrane permeability. Science > AP®︎/College Biology > Cell structure and function > Membrane permeability Cell Parts and Functions | Biology Dictionary WebMar 31, 2021 · Usually, a cell has a single nucleus that contains all of its DNA molecules, but some (such as skeletal muscle cells) have more than one nucleus. The nucleus protects the cell’s DNA while controlling all other cellular activities, such as cell division, growth, protein production, and cell death. The nucleus contains all the DNA of a cell Ribosomes Cell | Definition, Types, Functions, Diagram, Division ... - Britannica Webcell, in biology, the basic membrane-bound unit that contains the fundamental molecules of life and of which all living things are composed. A single cell is often a complete organism in itself, such as a bacterium or yeast. Other cells acquire specialized functions as they mature.
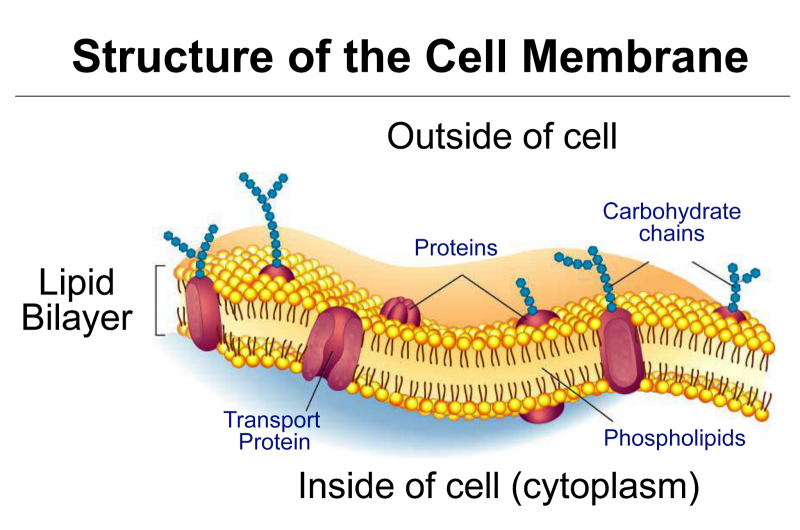
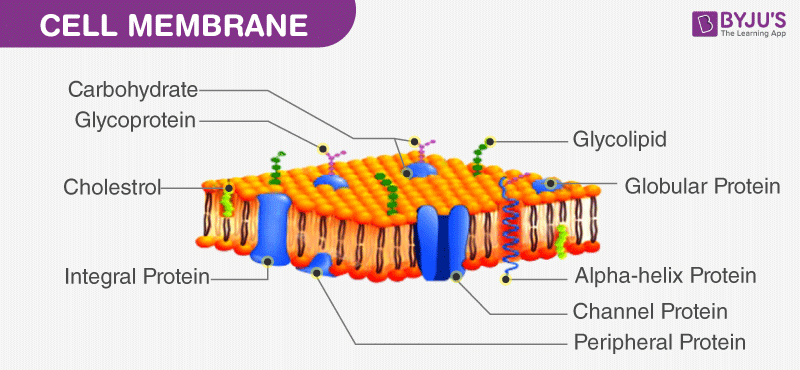
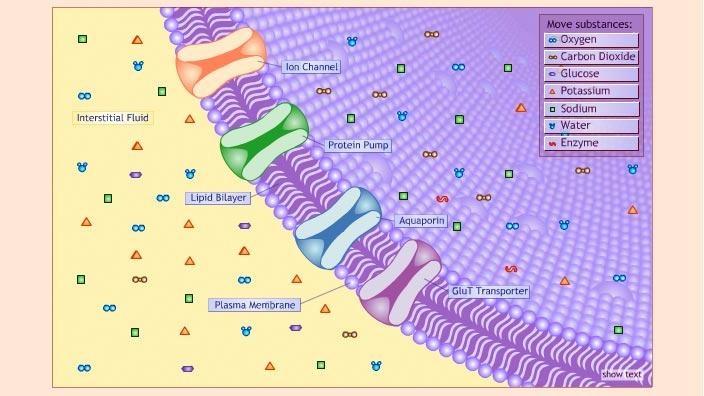
Cell membrane. Cell - Definition, Functions, Types and Examples | Biology Dictionary WebApr 28, 2017 · Cells are the basic unit of life. In the modern world, they are the smallest known world that performs all of life’s functions. All living organisms are either single cells, or are multicellular organisms composed of many cells working together. Cells are the smallest known unit that can accomplish all of these functions. What is a cell?: MedlinePlus Genetics WebCells are the basic building blocks of all living things. The human body is composed of trillions of cells. They provide structure for the body, take in nutrients from food, convert those nutrients into energy, and carry out specialized functions. Cell membrane introduction (video) | Khan Academy The cell membrane is what's on the outside of a cell. So if we have a very basic picture of a cell here with a little nucleus on the inside, this pink outside layer is what we call the cell membrane. The cell membrane can protect our cell from the outside environment, and it can determine what can enter and leave our cell. Cell membrane - Wikipedia The cell employs a number of transport mechanisms that involve biological membranes: 1. Passive osmosis and diffusion: Some substances (small molecules, ions) such as carbon dioxide (CO 2) and oxygen (O 2... 2. Transmembrane protein channels and transporters: Transmembrane proteins extend through ...
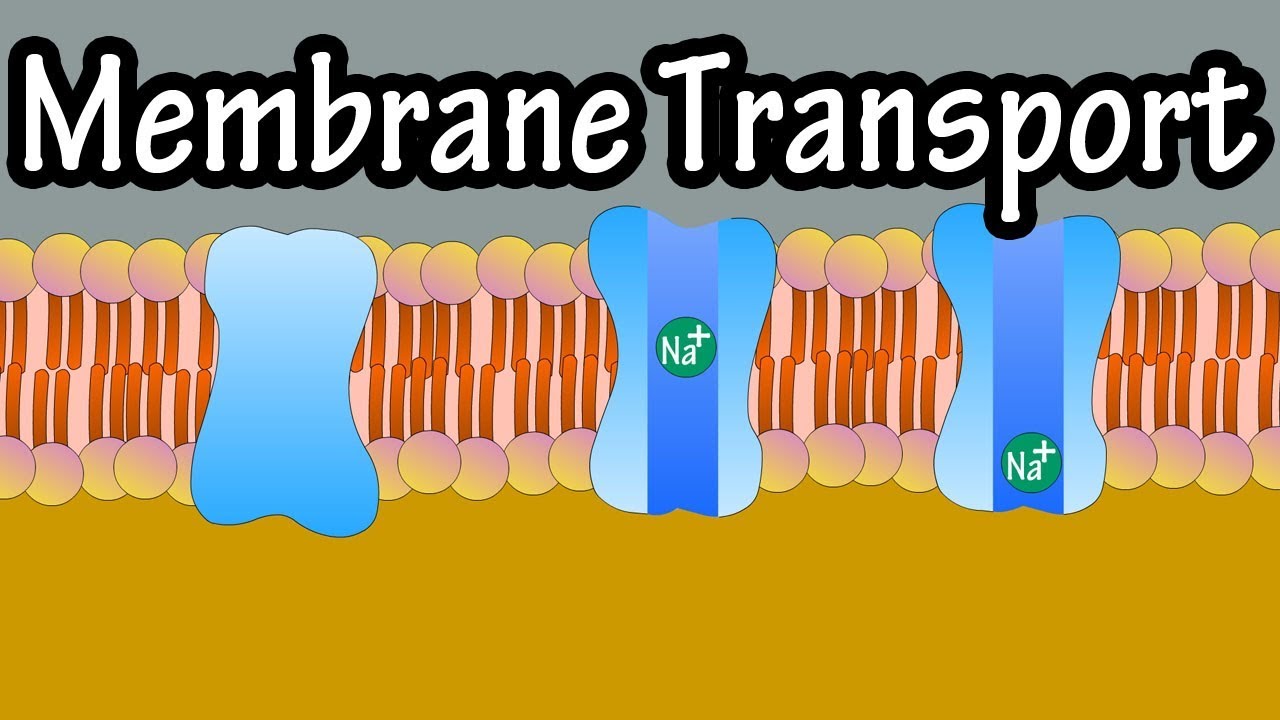
Cell - Rotten Tomatoes WebA graphic novelist (John Cusack) begins a desperate search for his estranged wife (Clark Sarullo) and son (Ethan Andrew Casto) after a mysterious cellphone signal transforms New Englanders into ... Cell Definition & Meaning - Merriam-Webster Web1. : a small religious house dependent on a monastery or convent. 2. a. : a one-room dwelling occupied by a solitary person (such as a hermit) b. : a single room (as in a … Cell | Journal | ScienceDirect.com by Elsevier WebJan 19, 2023 · Cell publishes findings of unusual significance in any area of experimental biology, including but not limited to cell biology, molecular biology, neuroscience, immunology, virology and microbiology, cancer, human genetics, systems biology, signaling, and disease mechanisms and therapeutics. The …. View full aims & scope. Passive transport and active transport across a cell membrane... Transport across a cell membrane. Transport across a cell membrane questions. Passive transport and active transport across a cell membrane article. How do things move across a cell membrane? Passive Transport by Facilitated Diffusion. Diffusion and osmosis. Exocytosis. Phagocytosis. Membrane potentials - part 1.
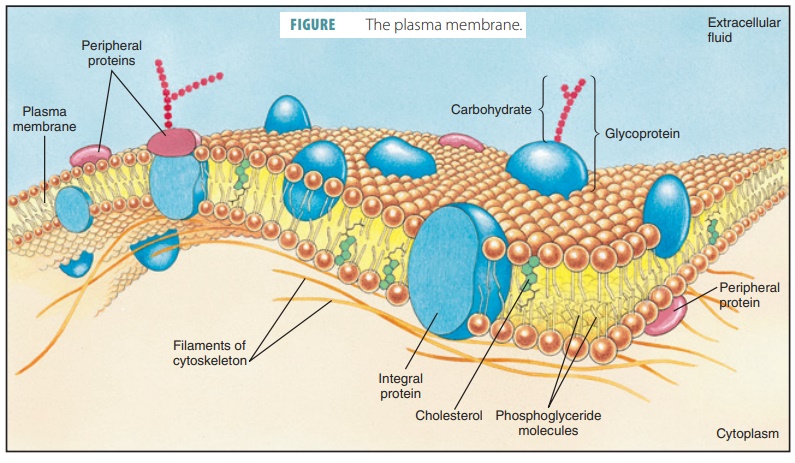
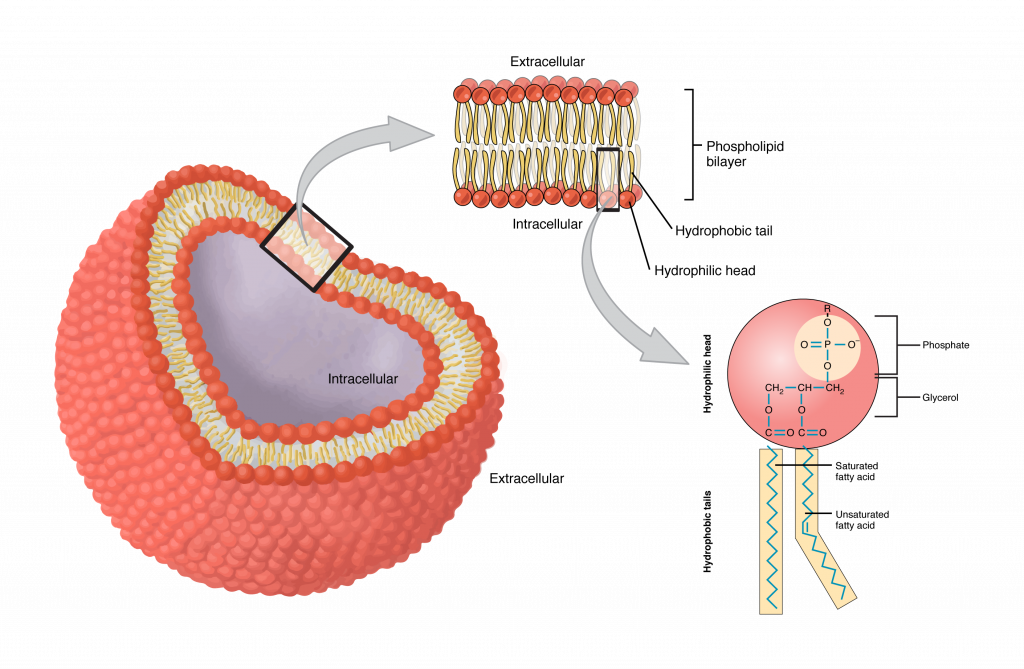
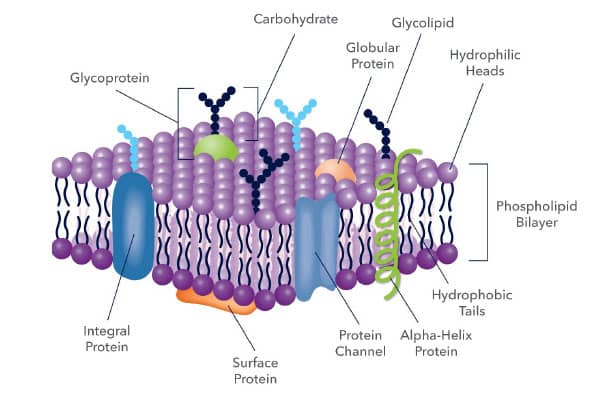
Home: Cell Press WebPublisher of over 50 scientific journals across the life, physical, earth, and health sciences, both independently and in partnership with scientific societies including Cell, Neuron, Immunity, Current Biology, AJHG, and the Trends Journals. Plasma Membrane (Cell Membrane) - Genome.gov Jan 20, 2023 · The plasma membrane, also called the cell membrane, is the membrane found in all cells that separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. In bacterial and plant cells, a cell wall is attached to the plasma membrane on its outside surface. The plasma membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable. 3.1 The Cell Membrane – Anatomy & Physiology This cell membrane provides a protective barrier around the cell and regulates which materials can pass in or out. Structure and Composition of the Cell Membrane. The cell membrane is an extremely pliable structure composed primarily of two layers of phospholipids (a “bilayer”). Cholesterol and various proteins are also embedded within the membrane giving the membrane a variety of functions described below. Cell | Definition, Types, Functions, Diagram, Division ... - Britannica Webcell, in biology, the basic membrane-bound unit that contains the fundamental molecules of life and of which all living things are composed. A single cell is often a complete organism in itself, such as a bacterium or yeast. Other cells acquire specialized functions as they mature.
Cell Parts and Functions | Biology Dictionary WebMar 31, 2021 · Usually, a cell has a single nucleus that contains all of its DNA molecules, but some (such as skeletal muscle cells) have more than one nucleus. The nucleus protects the cell’s DNA while controlling all other cellular activities, such as cell division, growth, protein production, and cell death. The nucleus contains all the DNA of a cell Ribosomes
Fluid mosaic model: cell membranes article (article) | Khan... Cell membrane introduction. Cell membrane overview and fluid mosaic model. Fluid mosaic model: cell membranes article. Plant cell walls. The extracellular matrix and cell wall. Membrane permeability. Science > AP®︎/College Biology > Cell structure and function > Membrane permeability





















Post a Comment for "40 cell membrane"